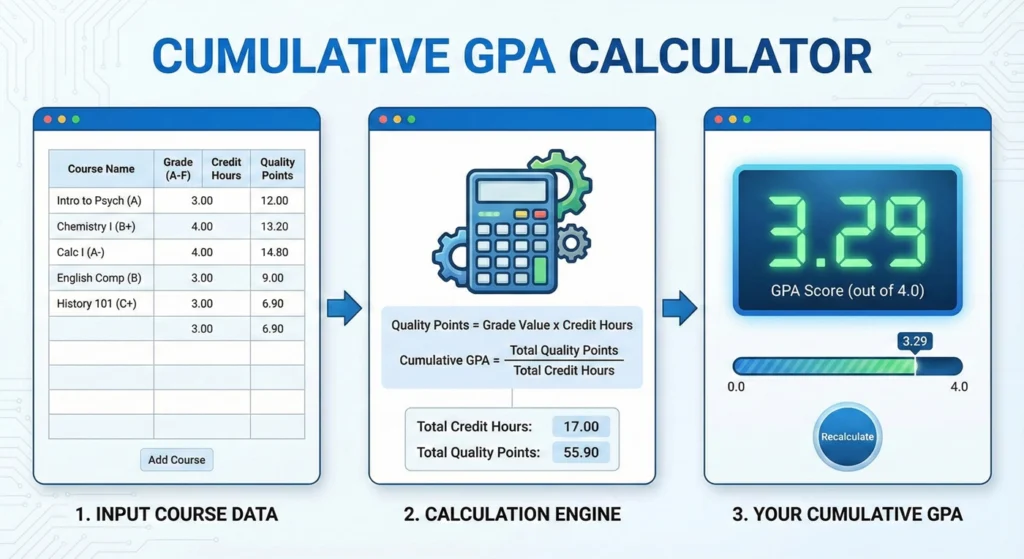
Have you ever stared at your transcript wondering why that A- feels so unfair? Or maybe you’ve been puzzling over how to calculate cumulative GPA with all those pluses and minuses throwing off your math? You’re not alone! The way colleges measure academic performance has undergone a major makeover in recent years, and understanding your cumulative GPA is more important (and complicated) than ever before.
Remember when grades were simple? An A was an A, a B was a B, and life made sense? Well, those days are long gone in most universities, replaced by a more nuanced—and sometimes frustrating—plus/minus grading system. This shift wasn’t just to make your life harder (though sometimes it feels that way!); it was actually implemented to provide a more precise measurement of your academic achievements.
Here’s the kicker though: research shows that after implementing plus/minus grading, GPAs actually declined overall, with “A” grades taking the biggest hit. Yep, that student fear that “plus/minus means lower grades” wasn’t just paranoia—the data backs it up!
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into the world of cumulative GPA calculators, explore why universities made this switch, and most importantly, help you understand what it means for your academic career. Whether you’re a grad student trying to maintain that crucial 3.5 or an undergrad just trying to figure out where you stand, this post has got you covered!
- Why Your Professor Ditched the Simple A-F System (And How It Affects Your Cumulative GPA)
- Real Talk: How Plus/Minus Grading Changed Grad Student GPAs
- What Professors Really Think vs. What Actually Happened
- The Behind-the-Scenes Drama of Changing Grading Systems
- What This All Means For Your Academic Future
- Final Thoughts on Navigating the Plus/Minus World
Why Your Professor Ditched the Simple A-F System (And How It Affects Your Cumulative GPA)
Why Traditional A-F Grading Was Considered “Too Coarse”
Let’s be real—the old A-F system was basically the academic equivalent of giving everyone either an “awesome,” “good,” “meh,” “yikes,” or “catastrophic” rating. Not exactly precision grading, right?
Professors had a legitimate beef with this system. Imagine two students in your class: one who absolutely crushed it with a 98% and another who squeaked by with a 90%. Under the old system, both get the same 4.0 for an A, despite a pretty significant performance gap. On the flip side, a student with an 89% (B) and one with an 80% (also B) would have wildly different actual performances but identical GPA impacts.
This “bunching” problem meant your cumulative GPA calculator couldn’t really differentiate between the student who consistently got high Bs and the one who barely escaped C-territory. Not exactly fair, is it?
The Standardized Decimal Equivalents (AKA: The Math Behind Your GPA Calculator)
When universities implement a plus/minus system, they establish specific decimal values for each grade level. This is the secret sauce that makes your cumulative GPA calculator work its magic. Here’s the breakdown most schools use:
- A = 4.00 (Still the gold standard!)
- A- = 3.667 (So close, yet so far…)
- B+ = 3.333 (Better than average, but not quite A material)
- B = 3.00 (The solid middle-ground performer)
- B- = 2.667 (Starting to slip a bit…)
- C+ = 2.333 (Hanging in there)
- C = 2.00 (Just getting by)
- C- = 1.667 (Danger zone for grad students!)
Fun fact: Many schools debated adding an A+ worth 4.333 points but ultimately decided against it to preserve the sanctity of the 4.0 scale. Sorry, overachievers—there’s no “A++” in college!
Real Talk: How Plus/Minus Grading Changed Grad Student GPAs
Overall Grade Point Average Trends
When universities first announced plus/minus grading, students collectively freaked out, convinced their GPAs would tank. Were they right? Well, kinda.
The research shows that overall Graduate GPAs (GGPAs) didn’t completely crash and burn after the switch, but they definitely took a hit in most areas. Your cumulative GPA calculator would indeed show slightly lower numbers on average after the switch—confirming what students suspected all along.
The Great “A” Grade Massacre
Here’s where things get real: the number of straight-up “A” grades took a nosedive after plus/minus grading came into play. Before, if you were doing A-level work, you got an A, period. Now, professors could distinguish between “barely A” work (A-) and “solid A” work.
The result? A dramatic decline in perfect 4.0 contributions to students’ cumulative GPA. Every academic discipline—from business to humanities—saw fewer “A” grades being handed out, with Education and Humanities/Arts professors being particularly stingy with those perfect scores.
Grade Variability Across Academic Disciplines (Or: Why Business Majors Got Lucky)
Not all departments embraced the new system with equal enthusiasm. In fact, if you’re a business major, you might have actually benefited from the switch! Business was the only area where the cumulative GPA actually increased after plus/minus implementation.
Meanwhile, if you were studying Applied Sciences, Communication, Education, Humanities/Arts, or Physical Sciences… well, I hope you weren’t counting on maintaining that perfect GPA. These fields saw the most significant decreases in overall grades.
What this means is that there’s no one-size-fits-all answer to “how to calculate cumulative GPA” impact after a plus/minus switch—it depends heavily on your field of study. This variability suggests that different academic areas have fundamentally different approaches to grading, which probably isn’t shocking news to anyone who’s ever compared notes with friends in different majors!
What Professors Really Think vs. What Actually Happened

Did the System Actually Improve Grading Accuracy?
When asked, most faculty members across disciplines were Team Plus/Minus, believing it gave them more tools to accurately assess student performance. They could finally distinguish between that student who participated enthusiastically but bombed the final (B+) and the one who aced all the tests but never said a word in class (A-).
Interestingly though, about a quarter of Business professors disagreed, feeling the new system didn’t actually improve accuracy. (Maybe that explains why Business GPAs went up while everyone else’s went down?)
Impact on Student Motivation: Who Benefits?
Here’s where your personal approach to learning matters. Faculty generally believed that the plus/minus system benefited “stronger” students—those high achievers who are motivated by small improvements and recognition of excellence. If you’re the type who pushes for every possible point, seeing that A- turn into an A might be just the motivation you need.
On the flip side, professors didn’t think the system helped struggling students much. In fact, data showed that students with undergraduate GPAs below 3.0 saw their graduate GPAs decline slightly more after implementation. Your cumulative GPA calculator might deliver some tough love if you’re already struggling academically.
Who Actually Used the New System?
Not all professors embraced the plus/minus revolution with equal enthusiasm. The research reveals some pretty interesting patterns:
- Assistant Professors (the younger crowd) used plus/minus grading way more (87.5%) than Full Professors (70%)
- Faculty with 1-4 years of experience used it considerably more (85.3%) than the veterans with 15+ years (69.7%)
In other words, if you wanted to avoid the plus/minus impact on your cumulative GPA, your best bet was to take classes with older, more established professors who were set in their A-F ways!
The Behind-the-Scenes Drama of Changing Grading Systems
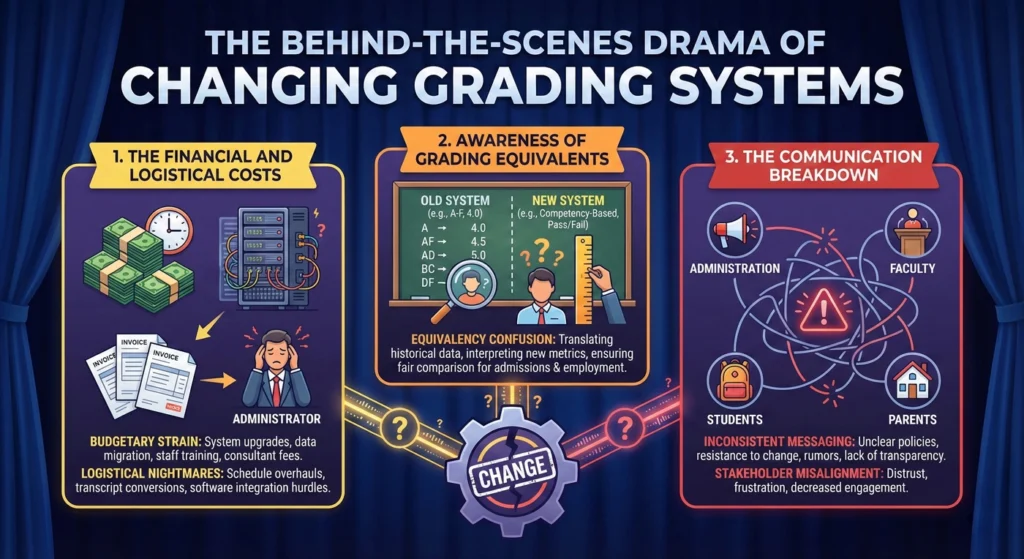
The Financial and Logistical Costs (Spoiler: It’s Not Cheap!)
Changing a university-wide grading system isn’t just flipping a switch. One institution estimated costs around $70,000 and over 600 work hours just to implement the change! That includes updating computer systems, forms, transcripts, and retraining administrative staff.
So next time you’re grumbling about that A- impacting your cumulative GPA calculator results, remember that the university paid good money for the privilege of giving you that minus!
Awareness of Grading Equivalents
Here’s a shocker: nearly 80% of faculty members didn’t actually know the specific decimal values assigned to each grade when computing cumulative GPA. Only about 16% included these equivalents on their syllabi.
In other words, many professors were giving out A-minuses without realizing they were worth 3.667 instead of 4.0! This knowledge gap might explain why some students felt blindsided when they calculated their semester GPA.
The Communication Breakdown
Perhaps the most telling finding: 77% of faculty members admitted they simply had no idea how students felt about the plus/minus system. Talk about a disconnect! While students were frantically recalculating their cumulative GPA with each new grade, professors weren’t even sure if students cared.
This highlights a crucial need for better communication between faculty and students about grading policies and their real-world impacts on academic standing.
What This All Means For Your Academic Future
The Bottom Line on Your Bottom Line (GPA)
If your school has recently switched or is considering switching to plus/minus grading, here’s what you should expect:
- Your overall cumulative GPA probably won’t change dramatically, but it might dip slightly
- Getting a perfect 4.0 will become significantly harder
- The impact will vary depending on your major and the age of your professors
- Using a precise cumulative GPA calculator becomes more important than ever
Advice for Universities Considering The Switch
For any university administrators who somehow stumbled upon this blog (hello there!), the research suggests you should do your homework before making the switch:
- Evaluate existing grading practices across different departments
- Survey both students and faculty about their grading philosophies
- Analyze actual grade distributions to predict likely impacts
- Communicate clearly about how cumulative GPA will be calculated
- Be prepared for some initial resistance and GPA declines
The Silver Lining
Despite the potential GPA hit, there’s something to be said for more precise grading. The goal of grades should ultimately be to reflect actual learning, not just sort students into five broad buckets.
A plus/minus system gives professors more flexibility while still allowing those who prefer the traditional approach to stick with whole letter grades. For students truly concerned with learning (rather than just grades), this increased precision can provide more meaningful feedback.
Plus, knowing exactly how to calculate cumulative GPA with pluses and minuses is a valuable skill that will serve you throughout your academic career!
Final Thoughts on Navigating the Plus/Minus World
The shift to plus/minus grading represents higher education’s attempt to provide more nuanced assessment, even if it sometimes feels like they’re just finding new ways to lower your GPA. Understanding how these systems work—and having a reliable cumulative GPA calculator bookmarked—is essential for any student trying to keep track of their academic standing.
Remember that at the end of the day, your GPA is just one measure of your academic journey. While it’s important (especially for grad school applications and certain jobs), it’s not the only thing that matters. Focus on genuine learning, and those pluses and minuses will take care of themselves.
Need help calculating your GPA with all those pluses and minuses? Check out our free online Cumulative GPA Calculator tool to get an accurate picture of where you stand academically!