Hey there, friend! So you’ve probably heard everyone and their personal trainer talking about protein for weight loss, right? And honestly, they’re onto something. Protein isn’t just some trendy macronutrient that fitness influencers rave about—it’s actually a legit game-changer when it comes to dropping pounds and feeling amazing while doing it.
Here’s the thing: I’m going to walk you through everything you need to know about using protein to support your weight loss journey, and it’s all backed by actual science (you know, the peer-reviewed studies, medical associations, and academic research kind of stuff). But before we dive in, quick disclaimer—and this is super important—this information is for educational purposes only and doesn’t replace professional medical advice. Always chat with your doctor before making major changes to your diet, especially if you’ve got health conditions or are taking medications. Your healthcare provider knows your unique situation best!
Now that we’ve got that covered, let’s get into why protein might just become your new best friend on this weight loss adventure.
- 5 Science-Backed Ways Protein Supports Fat Loss
- Defining Your Optimal Daily Protein Requirements
- The Essential List of High-Protein Foods for Fat Loss
- Integrating Protein Powders and Shakes into Your Weight Loss Plan
- Important Safety Considerations for High Protein Intake
- The Bottom Line: Your Protein Action Plan
5 Science-Backed Ways Protein Supports Fat Loss

Okay, so why does protein work so well for weight loss? It’s not magic (spoiler alert: nothing is!), but it’s pretty darn close. Here are five legit reasons backed by science:
Increased Satiety and Appetite Control
Ever notice how a big bowl of pasta leaves you hungry an hour later, but a chicken breast keeps you satisfied for ages? That’s protein doing its thing. When you eat protein, it triggers the release of hormones that basically tell your brain, “Hey, we’re good here—no need to raid the fridge!”
Studies show that protein is way more filling than carbs or fats, gram for gram. This means you’ll naturally eat less throughout the day without feeling like you’re white-knuckling your way through hunger pangs. And let’s be real—nobody can stick to a diet where they’re constantly starving. How much protein for weight loss helps with this? We’ll get to the numbers soon, but just know that bumping up your protein intake can seriously curb those snack attacks.
Boosting Metabolism via the Thermic Effect of Food (TEF)
Here’s something cool: your body actually burns calories just digesting food. Wild, right? This is called the thermic effect of food, and protein is the heavyweight champion here. While your body uses about 5-10% of calories to digest carbs and 0-3% for fats, it burns a whopping 20-30% of protein calories just breaking it down!
So if you eat 100 calories of protein, your body burns about 25-30 of those just processing it. It’s like getting a mini metabolism boost with every high-protein meal. Not too shabby!
Muscle Preservation (Preventing Sarcopenic Obesity)
When you’re cutting calories to lose weight, your body doesn’t just burn fat—it can also break down muscle tissue for energy. And trust me, you don’t want that. Muscle is metabolically active, meaning it burns calories even when you’re binge-watching Netflix. The more muscle you maintain, the higher your metabolism stays.
This is especially crucial if you’re dealing with something called sarcopenic obesity—basically when you have both excess body fat and low muscle mass. It’s more common than you’d think, especially as we age. Eating enough protein while losing weight helps preserve that precious muscle tissue, so you’re losing fat, not the good stuff.
Stabilizing Blood Glucose Levels
Protein plays nice with your blood sugar. When you eat protein along with carbs, it slows down how quickly those carbs hit your bloodstream. This means fewer blood sugar spikes and crashes, which translates to more stable energy levels and less of those “I need sugar RIGHT NOW” moments.
Stable blood sugar also means your body isn’t pumping out tons of insulin, which can actually promote fat storage. So protein helps keep everything on an even keel, making it easier to stick to your weight loss plan.
Hormonal Regulation
Protein influences a whole bunch of hormones related to hunger and fullness. It increases levels of hormones like GLP-1, peptide YY, and cholecystokinin (try saying that five times fast!), which all make you feel satisfied. At the same time, it lowers ghrelin, the hormone that makes your stomach growl and sends you searching for snacks.
Basically, protein works behind the scenes to make your body’s hunger signals work in your favor instead of against you.
Defining Your Optimal Daily Protein Requirements

Alright, so how much protein should you actually be eating? This is where things get interesting because the answer isn’t one-size-fits-all.
General Guidelines vs. Weight Loss Goals
The standard RDA (Recommended Dietary Allowance) for protein is about 0.8 grams per kilogram of body weight, or roughly 0.36 grams per pound. For a 150-pound person, that’s only about 54 grams per day. And honestly? That’s just enough to prevent deficiency—it’s not optimized for weight loss or body transformation.
For weight loss, research suggests bumping that up significantly—more like 1.2 to 2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight (about 0.5 to 1 gram per pound). So that same 150-pound person would be looking at 75-150 grams of protein daily. That’s a pretty big range, I know, but your sweet spot depends on factors like your activity level, age, and how aggressive your calorie deficit is.
Calculating Protein Intake for Obese or Overweight Individuals
Here’s where it gets a bit tricky. If you’re significantly overweight, you don’t want to calculate your protein needs based on your current weight—that would give you a crazy high number. Instead, aim for protein based on your goal weight or lean body mass.
A good rule of thumb: shoot for about 1.2-1.6 grams per kilogram of your ideal body weight. So if your goal is 160 pounds (about 73 kg), you’d aim for roughly 88-117 grams of protein per day. This ensures you’re getting enough to preserve muscle and feel satisfied without going overboard.
People who’ve had bariatric surgery have even higher protein needs—usually 60-80 grams minimum, and sometimes up to 100+ grams, depending on the procedure. If that’s you, definitely work closely with your medical team on this!
Timing Matters: Defining Protein Needs per Meal
It’s not just about the total—when you eat protein matters too. Your body can only use so much protein at once for muscle maintenance and synthesis. Research suggests aiming for about 25-40 grams per meal, spread across 3-4 meals throughout the day.
Quick Reference Guide:
- Breakfast: 25-30g protein (sets you up for better appetite control all day)
- Lunch: 30-40g protein (keeps energy stable through the afternoon slump)
- Dinner: 30-40g protein (supports overnight muscle recovery)
- Snacks (if needed): 10-20g protein
This distribution keeps your metabolism humming and helps with muscle maintenance throughout the day.
The Essential List of High-Protein Foods for Fat Loss
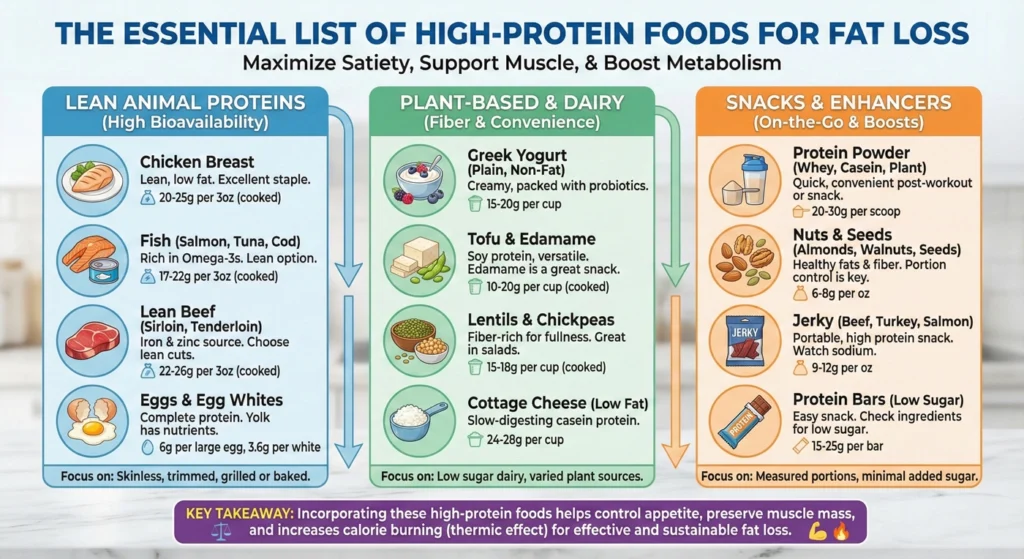
So what should you actually eat? Let me break down some fantastic options that’ll help you hit those protein goals without getting bored.
Lean Animal-Based Proteins
These are your protein powerhouses—they’re complete proteins (meaning they have all the essential amino acids) and pack a serious punch:
Poultry: Chicken breast gives you about 31g protein per 3.5 oz serving, while turkey breast is similar. They’re lean, versatile, and budget-friendly.
Fish and Seafood: Salmon packs about 25g per 3.5 oz (plus those omega-3s!), tuna has around 30g, and shrimp gives you about 24g. Bonus: most fish is lower in calories than meat.
Lean Meats: Lean beef has about 26g per 3.5 oz, pork tenderloin has around 26g, and bison is even leaner with similar protein content.
Eggs: One large egg has 6g protein. They’re cheap, easy, and incredibly versatile. The yolk has nutrients too, so don’t just eat whites!
Dairy: Greek yogurt is a superstar with 15-20g per cup, cottage cheese has about 14g per half cup, and even regular milk gives you 8g per cup.
The Best Plant-Based Proteins for Complete Amino Acid Profiles
Plant proteins are awesome, but here’s the catch: most are “incomplete,” meaning they’re missing one or more essential amino acids. The solution? Mix and match! When you combine different plant proteins, you create complete amino acid profiles.
Legumes: Lentils pack 18g protein per cooked cup, black beans have about 15g, and chickpeas give you 15g. They’re also loaded with fiber, which helps with weight loss too.
Soy Products: Tofu has 10-20g per 3.5 oz (depending on firmness), tempeh has about 19g, and edamame gives you 17g per cup. Soy is actually a complete protein, which is pretty cool!
Whole Grains: Quinoa (8g per cooked cup) is a complete protein, soba noodles have about 12g per 3 oz, and even wheat germ packs 6g per ounce. These aren’t just for carbs!
Nuts and Seeds: Almonds have 6g per ounce, pumpkin seeds have 7g, and hemp seeds pack 10g per 3 tablespoons. Plus they have healthy fats.
Vegetables: Yeah, veggies have protein too! Green peas have 8g per cup, spinach has 5g per cooked cup, and broccoli gives you 4g per cup.
Protein-Rich Snacks and Meal Replacements
Sometimes you need something quick and portable. Here are some great options:
- Protein bars: Look for ones with 15-20g protein and minimal added sugar
- Jerky: Beef, turkey, or salmon jerky (watch the sodium though!)
- Protein balls: Homemade with protein powder, oats, and nut butter
- Hard-boiled eggs: Nature’s perfect portable protein
- String cheese: About 6-7g protein per stick
- Roasted chickpeas: Crunchy, satisfying, and about 15g protein per cup
Integrating Protein Powders and Shakes into Your Weight Loss Plan

Let’s talk about the best protein powder for weight loss, because sometimes whole foods alone don’t cut it—or you just need something super convenient.
Benefits of Protein Shakes for Weight Loss
Protein shakes are clutch when you’re busy or struggling to hit your protein targets. They’re:
- Convenient: Mix and go in 30 seconds
- Precise: You know exactly how much protein you’re getting
- Low-calorie: Most powders give you 20-30g protein for only 100-150 calories
- Versatile: Blend into smoothies, add to oatmeal, or make protein pancakes
Some people use them as meal replacements, which can work for weight loss if done right—just make sure you’re getting enough nutrients from your other meals.
Comparison: Whey vs. Soy Protein
So which is better—whey or soy protein? Honestly, both are great options, and the research shows pretty similar results for weight loss and body composition.
Whey protein is derived from dairy, digests quickly, and has an excellent amino acid profile. It’s often considered the gold standard. Most studies show it’s effective for muscle maintenance during weight loss.
Soy protein is plant-based, so it’s perfect for vegans and people with dairy sensitivities. Meta-analyses comparing whey and soy show that both effectively support muscle retention and weight loss. The differences are pretty minor—it really comes down to personal preference and dietary restrictions.
Other options include casein (slower-digesting), pea protein (great for vegans), brown rice protein, and blends. Experiment to find what tastes good to you and agrees with your stomach.
Dietitian-Approved Selection Criteria
When shopping for the best protein powder for weight loss, look for:
- At least 20g protein per serving: Anything less isn’t worth it
- Low sugar: Under 5g per serving (ideally less)
- Minimal ingredients: Can you pronounce most of them?
- Third-party tested: Look for labels like NSF Certified or Informed-Sport
- Good taste: Seriously, if it tastes like chalk, you won’t use it
- Fits your needs: Low-carb if you’re doing keto, vegan if that’s your thing, etc.
Taste-test a few! Many companies offer sample packs so you don’t have to commit to a giant tub of something gross.
Important Safety Considerations for High Protein Intake

Okay, real talk time. While protein is generally safe and awesome, there are some things you should know.
Understanding Adverse Effects
For most healthy people, eating high amounts of protein (up to 2g per kilogram of body weight) is perfectly safe. But there are some potential issues to be aware of:
Kidney concerns: If you have existing kidney disease, high protein intake can be problematic. For healthy people, there’s no evidence that normal high-protein diets damage kidneys, but if you have any kidney issues, definitely talk to your doctor before significantly increasing protein.
Digestive issues: Suddenly ramping up protein can cause constipation, especially if you’re not drinking enough water or getting enough fiber. Start gradually and stay hydrated!
Nutrient balance: Going too extreme with protein can crowd out other important nutrients. You still need healthy fats, fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Balance is key!
Bone health myths: Old research suggested high protein might hurt bone health, but newer studies actually show the opposite—adequate protein supports strong bones, especially as we age.
The NIH notes that protein intakes above the RDA are generally well-tolerated in healthy adults, but individual needs and tolerances vary.
Consulting Medical Professionals
I can’t stress this enough: always consult with your doctor or a registered dietitian before making major dietary changes, especially if you:
- Have kidney disease or kidney problems
- Have liver disease
- Are pregnant or breastfeeding
- Have diabetes
- Are taking medications (some can interact with dietary changes)
- Have any chronic health conditions
Your healthcare provider can help you determine the right amount of protein for your specific situation and monitor any potential issues. This is especially important since nutrition is a YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) topic—getting it wrong can have real health consequences.
Frequently Asked Questions
Let me tackle some common questions I get all the time:
Can a high-protein diet improve overall health, beyond weight loss?
Absolutely! Beyond helping you lose weight, adequate protein intake supports immune function, wound healing, healthy aging, maintaining strong bones, and even better mood (your brain needs amino acids to make neurotransmitters). Some research suggests it may help with blood pressure and cardiovascular health too. Pretty cool, right?
Are proteins magic wands for weight loss?
Haha, no—I wish! Protein is an incredibly helpful tool, but it’s not magic. You can’t eat unlimited protein, ignore calories, skip exercise, and expect the pounds to melt off. Protein works best when combined with a balanced diet, appropriate calorie deficit, regular movement, good sleep, and stress management. Think of it as a powerful ally in your weight loss journey, not a miracle cure.
Is it safe to use meal replacement shakes for weight loss?
It can be safe when done properly! Meal replacement shakes can be a convenient tool, but I wouldn’t recommend replacing more than 1-2 meals per day, and definitely not long-term. You need the variety of nutrients that whole foods provide. If you’re going this route, choose high-quality shakes with added vitamins and minerals, and make sure your other meals are nutrient-dense. And again—run it by your doctor or dietitian first, especially if you have health conditions.
What is the risk of high protein intake?
For healthy people, the risks are minimal when protein intake is reasonable (under 2-2.5g per kg of body weight). The main concerns are digestive discomfort if you ramp up too quickly, potential issues for people with pre-existing kidney disease, and the risk of nutritional imbalance if protein crowds out other important foods. Stay hydrated, eat plenty of fiber-rich foods, and don’t go to extremes. Moderation and balance are your friends!
The Bottom Line: Your Protein Action Plan
Alright, let’s wrap this up with a game plan! Protein for weight loss isn’t complicated—it just requires a bit of planning and consistency.
Your action steps:
- Calculate your target: Aim for 1.2-2.0g per kg of goal body weight, spread across 3-4 meals
- Choose quality sources: Mix animal and/or plant proteins based on your preferences
- Plan ahead: Prep protein-rich foods for the week so you’re never scrambling
- Consider supplements: Add a quality protein powder if whole foods alone aren’t cutting it
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water, especially with higher protein intake
- Monitor how you feel: Adjust based on your energy, hunger, and results
- Talk to your doc: Get professional guidance, especially if you have health conditions
Remember, sustainable weight loss is a marathon, not a sprint. Protein is an amazing tool that can make the journey easier, keep you feeling satisfied, and help you maintain that hard-earned muscle. But it works best as part of a balanced, enjoyable approach to eating that you can stick with long-term.
You’ve got this! And hey, if you learned something new or found this helpful, I’d love to hear about your protein-powered weight loss journey. Here’s to feeling stronger, healthier, and more energized!
Sources and Further Reading: This article is based on peer-reviewed research from sources including the National Institutes of Health (NIH), academic journals on nutrition and metabolism, and evidence-based dietary guidelines. For specific medical advice tailored to your situation, please consult with healthcare professionals.